Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tateishi, Ryo*; Shimada, Koji; Shimizu, Mayuko; Ueki, Tadamasa*; Niwa, Masakazu; Sueoka, Shigeru; Ishimaru, Tsuneari
Oyo Chishitsu, 62(2), p.104 - 112, 2021/06
We attempted to discriminate between active and non-active faults by linear discriminant analysis using the chemical composition data of fault gouges in Japan, and then examined the elements that represent the difference between them and better discriminants. As a result, the multiple discriminants obtained could discriminate between them with high probability. In addition, the generalization performance of these discriminants is discussed, and the discriminants that can be expected to have high discriminant performance for unknown samples are presented. Also, from the combination of elements common to these discriminants, we narrowed down the number of elements that represent the difference between active and non-active faults to 6, and showed that the combination of TiO and Sr contributing the most to the discrimination. The method applied in this study is an innovative one that can discriminate the activity by chemical analysis of fault rocks that are universally present in the bedrock.
and Sr contributing the most to the discrimination. The method applied in this study is an innovative one that can discriminate the activity by chemical analysis of fault rocks that are universally present in the bedrock.
Matsuda, Asahi*; Takahashi, Satoru*; Kawabata, Kuniaki; Takemura, Fumiaki*; Ogasawara, Kei*
no journal, ,
In recent years, research of bleaching of coral based on change of underwater environment is important in order to know change of global environment. Currently, investigation of underwater is conducted by the diver. Therefore, several problems such as load for the diver and restriction of search area are occurred. To solve these problems, we are developing the underwater robot for investigating of coral reef for the wide and the long time. In here, to know the current situation of coral we consider the automatic extraction method of the coral based on texture analysis from image obtained by monitoring.
Tateishi, Ryo*; Shimada, Koji; Shimizu, Mayuko; Sueoka, Shigeru; Niwa, Masakazu; Ishimaru, Tsuneari
no journal, ,
The identification of active faults is based on the displacement and deformation of the current topography and the late Quaternary strata. However, in the absence of them, it is difficult to determine the fault activity. To solve this problem, multivariate analysis was performed using chemical composition data of fault gouges of active and inactive faults in Japan. We performed linear discriminant analysis with a following combination of elements; (a) 11 elements selected by AIC, (b) 8 elements with p-value between 0 and 0.01, (c) 6 elements with p-value between 0 and 0.001. The discrimination rate between active faults and inactive faults is 100% in (a), (b) and 97% in (c). Among elements that represent the difference, TiO and P
and P O
O , and Al
, and Al O
O and Rb are considered important, including their respective combinations. These results contribute to clarify the mechanism that creates the difference in chemical composition between active and inactive faults.
and Rb are considered important, including their respective combinations. These results contribute to clarify the mechanism that creates the difference in chemical composition between active and inactive faults.
Tateishi, Ryo*; Shimada, Koji; Niwa, Masakazu; Sueoka, Shigeru; Shimizu, Mayuko; Kanno, Mizuho; Ishii, Chikako; Ishimaru, Tsuneari
no journal, ,
The major difference between active faults and inactive faults is the elapsed time after the latest activity, and while active faults are considered to be on the order of 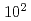 to
to 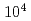 years, inactive faults are over
years, inactive faults are over 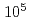 years. Therefore, even if the phenomena caused by fault activity are the same in both cases, the chemical changes that occur during the subsequent rest period of fault activity may differ significantly. In this study, the chemical composition of fault clay was collected by literature values and actual analysis, and the feasibility of discrimination by the chemical composition examined by linear discriminant analysis. According to the 11 elements selected based on the AIC, 45 active fault samples and 51 inactive fault samples were identified with a discrimination rate of 96%. Among the elements, TiO
years. Therefore, even if the phenomena caused by fault activity are the same in both cases, the chemical changes that occur during the subsequent rest period of fault activity may differ significantly. In this study, the chemical composition of fault clay was collected by literature values and actual analysis, and the feasibility of discrimination by the chemical composition examined by linear discriminant analysis. According to the 11 elements selected based on the AIC, 45 active fault samples and 51 inactive fault samples were identified with a discrimination rate of 96%. Among the elements, TiO and P
and P O
O tended to be concentrated as the latest activity period was newer. These concentration mechanisms are for future work.
tended to be concentrated as the latest activity period was newer. These concentration mechanisms are for future work.